What Foods Contain Astaxanthin | Health Secret of the Sea
Get the scoop on 'What Foods Contain Astaxanthin' and why this nutrient is a game-changer for your health.
Have you ever wondered why flamingos are pink or why cooked lobsters turn red?
The secret lies in a powerful antioxidant called astaxanthin.
Not only does it give certain animals their vibrant hues, but it also offers numerous health benefits for us humans.
Let's dive into the world of astaxanthin and explore the foods that are rich in this amazing compound.
What is Astaxanthin?
It belongs to the same family as beta-carotene (you know, the stuff that makes carrots orange) and lycopene (the red pigment in tomatoes).
However, astaxanthin is unique due to its superior antioxidant properties.
Let's think of antioxidants as the body's little helpers that protect our cells from damage. They're like the shields in a video game, warding off attacks from harmful free radicals.
- Among the antioxidant family, astaxanthin is often referred to as the 'king' because it is 10 times stronger than other carotenoids like beta-carotene and up to 1,000 times more effective than Vitamin E.
- Research has linked astaxanthin to a number of health benefits. It supports healthy skin, aids in eye health, boosts the immune system, and even helps improve athletic performance.
The Science Behind Astaxanthin
So how does astaxanthin work?
Imagine your body as a bustling city. Just like a city, your body produces waste - these are the free radicals.
If they're not taken care of properly, they start causing problems - think of it as pollution in the city.
Astaxanthin, the superhero antioxidant, swoops in and neutralizes these free radicals, preventing them from causing cellular damage. It's like a super-powered cleanup crew, maintaining the balance and ensuring the city (your body) continues to function smoothly.
- Scientific research supports the beneficial effects of astaxanthin. A recent study found that astaxanthin can help reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and helps protect the immune system.
- Another study in the journal Marine Drugs pointed out that astaxanthin could help slow down skin aging.
Top Foods Rich in Astaxanthin
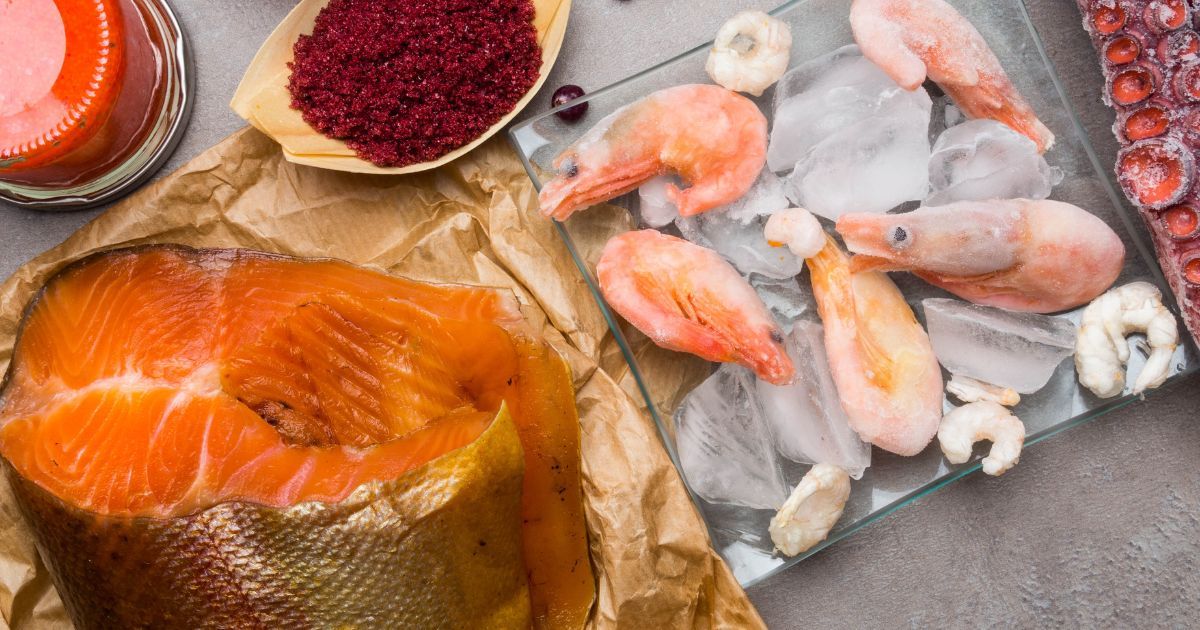

Ready to dive into the deep blue sea of astaxanthin-rich foods? Let's navigate through the ocean of options where you can source this antioxidant powerhouse from.
Seafood Sources
The ocean is brimming with a plethora of creatures that are rich in astaxanthin. Think of it as a treasure chest, full of colorful, health-boosting gems. Let's explore some of these sea treasures:
Salmon
Salmon is like the superstar of the seafood world when it comes to astaxanthin content.
- Sockeye salmon in particular, renowned for its rich red color, boasts a high astaxanthin content, with studies revealing a range of 26-38 mg per kg of flesh.
- Salmon is also a rich source of the essential fatty acid Omega-3. In fact, it's one of the highest sources of Omega-3s among all foods. On average, a serving of salmon can contain up to 2,150 mg of Omega-3 fatty acids.
Shrimp
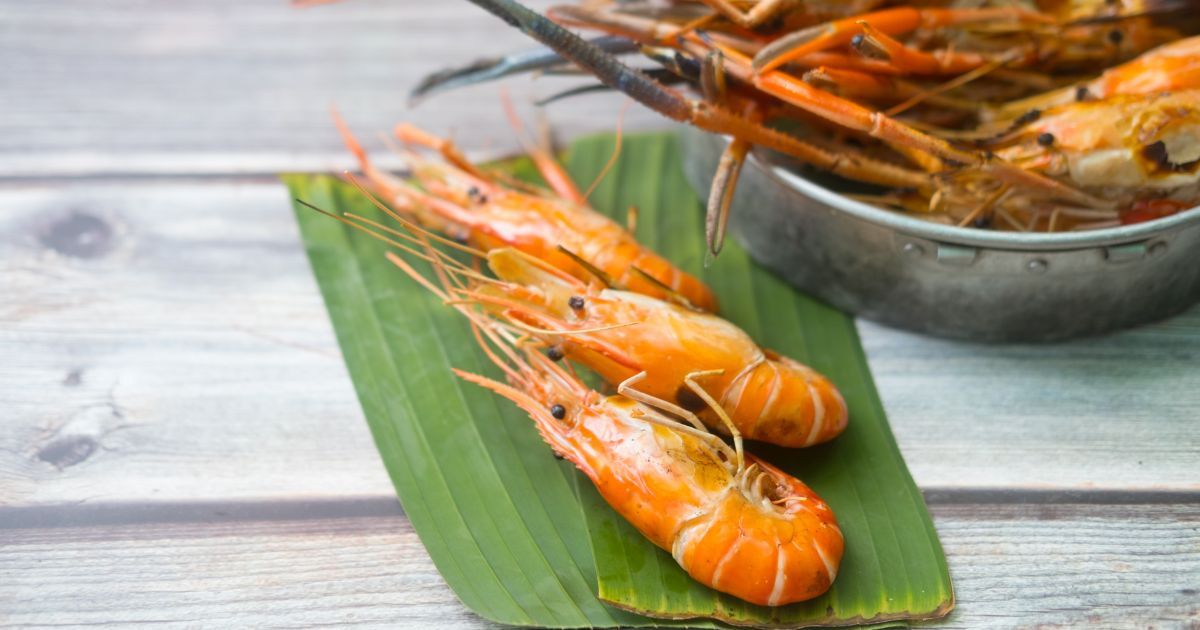

Shrimp may be small in size, but they're giants in the astaxanthin department.
- They absorb astaxanthin from their diet, which gives them their pinkish-red hue when cooked.
- Shrimp feed on a diet rich in astaxanthin-containing sources like krill and certain types of algae, resulting in shrimp flesh that contains approximately 1-3 mg of astaxanthin per kg.
Krill
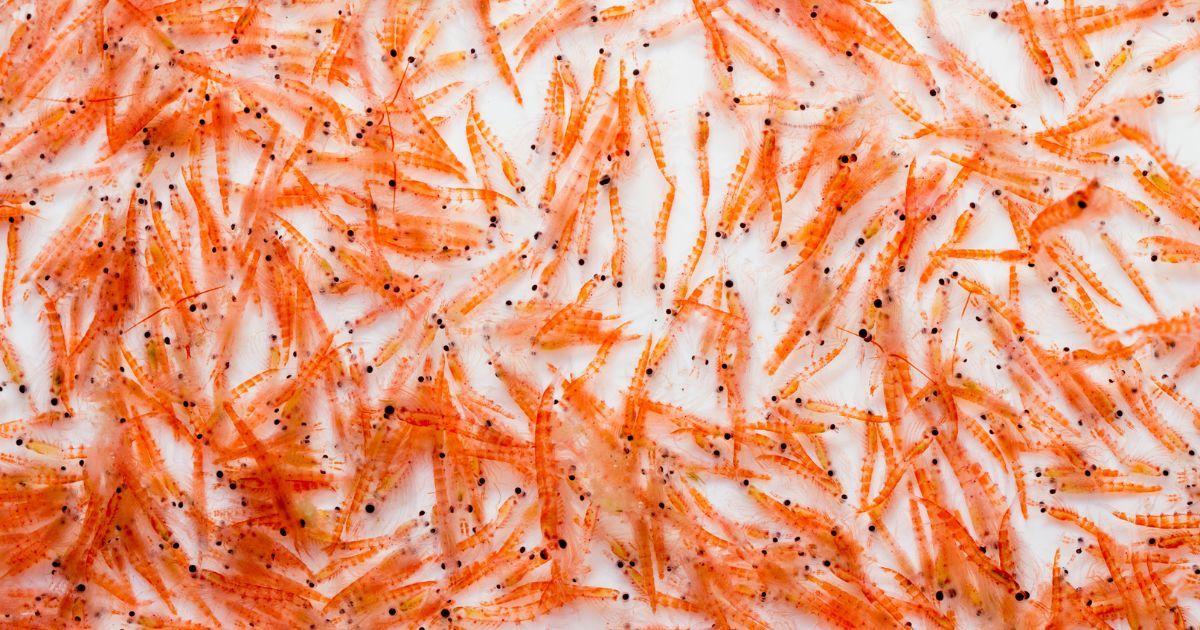

Krill are tiny crustaceans that serve as a significant food source for larger marine animals.
- Much like shrimp, krill get their astaxanthin from the phytoplankton they eat.
- Krill oil is often marketed as a supplement due to its high astaxanthin content.
Lobster
Next time you indulge in a lobster dinner, remember you're also getting a good dose of astaxanthin.
- Lobsters consume a varied diet that includes astaxanthin-rich foods such as small fish and crustaceans, which contributes to their characteristic color.
- However, the astaxanthin content in lobster meat is relatively lower, with an average of about 0.5-1 mg per kg.
Crab
Crabs, much like other crustaceans, are another excellent source of astaxanthin.
- Whether you prefer king crab, snow crab, or blue crab, rest assured you're reaping the astaxanthin benefits.
- Crabs feast on a variety of foods including algae, plankton, mollusks, and small fish, many of which are rich in astaxanthin, contributing to the bright color seen in cooked crab meat.
- While the exact amount can vary, crab meat typically contains approximately 0.5-2 mg of astaxanthin per kg.
Trout and Red Seabream
Other fish species such as trout and Red Seabream are also known to contain astaxanthin. It's like a game of 'I Spy' - generally, the pinker or redder the flesh, the higher the astaxanthin content!
Algae and Fungi Sources

Beyond the sea, certain types of algae and fungi also produce astaxanthin. They're like the unsung heroes in the astaxanthin world.
Haematococcus Pluvialis Algae
This freshwater green algae is the most abundant natural source of astaxanthin. When conditions get tough (like low nutrients or intense sunlight), the algae ramps up its astaxanthin production, turning from green to a deep red.
Red Yeast (Phaffia Rhodozyma)
Red yeast, a type of fungus, is another natural producer of astaxanthin. It's often used in the aquaculture industry to enhance the red-pink colors of farmed seafood.
The Flamingo Connection
Believe it or not, flamingos aren't born with their iconic pink plumage.
In fact, baby flamingos are born with grey feathers. So how do they get their pink glow?
You guessed it - astaxanthin!
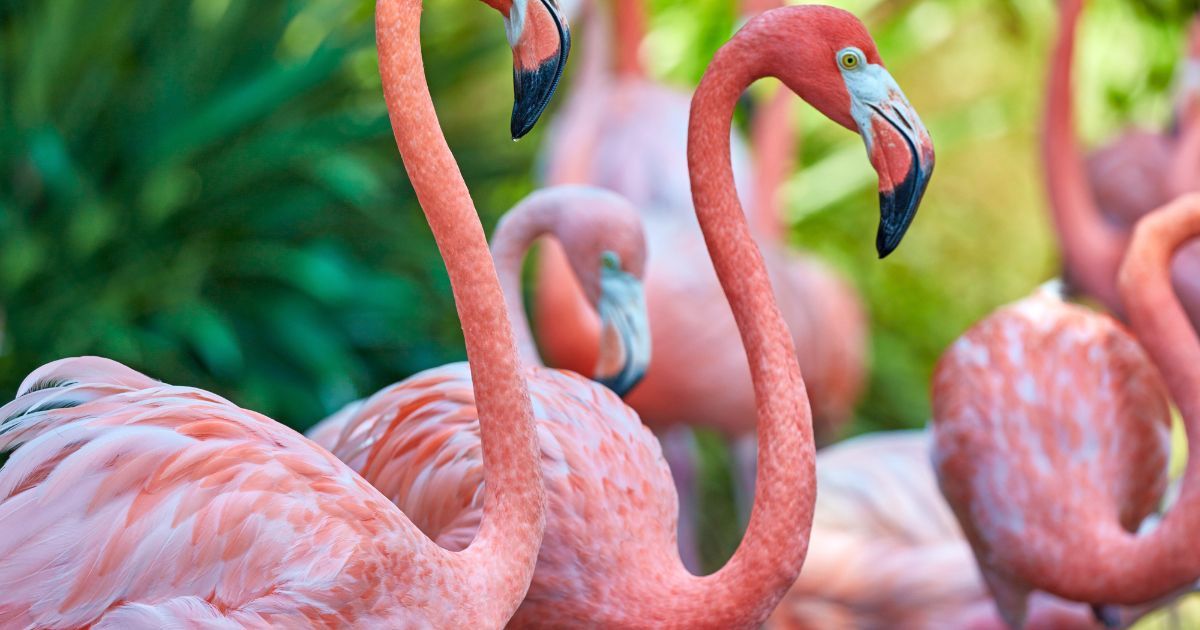

- As they continuously consume these astaxanthin-rich foods, the pigment accumulates in their feathers, giving them their signature pink color.
Think of it as nature's way of 'you are what you eat'. Just like how eating lots of carrots can turn your skin a bit orange, the astaxanthin in a flamingo's diet transforms their feathers from grey to gorgeous pink.
The Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin isn't just a fancy word; it's a health-boosting powerhouse! This potent antioxidant has been linked to a plethora of health benefits.
Let's dive into some of the ways astaxanthin can contribute to your well-being.
Powerful Antioxidant
As an antioxidant, astaxanthin helps combat oxidative stress in the body, which can reduce inflammation and help protect against various diseases, including heart disease and cancer.
- Studies indicate that taking astaxanthin and vitamin C simultaneously can boost their combined antioxidant properties, making them an effective combination for promoting health and well-being.
Skin Health

Think of it as nature's sunscreen, providing a layer of protection for your skin.
Eye Health
Astaxanthin has also been shown to support eye health. It can potentially reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and other eye-related problems.
Boosts Exercise Performance
For the fitness enthusiasts out there, astaxanthin might be your new workout buddy. Some studies suggest that it can improve exercise performance and recovery, thanks to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Supports Heart Health
Astaxanthin may also offer heart-healthy benefits. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, it could potentially lower the risk of heart disease and improve cardiovascular health.
Enhances Brain Health
Emerging research suggests that astaxanthin may have neuroprotective effects, potentially slowing down cognitive decline and reducing the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Remember, while astaxanthin is powerful, it's not a magic bullet. It should be part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
How To Incorporate Astaxanthin-Rich Foods Into Your Diet
Now that we've surfed through the astaxanthin-rich foods available, let's explore how you can add these nutritious treasures to your diet.
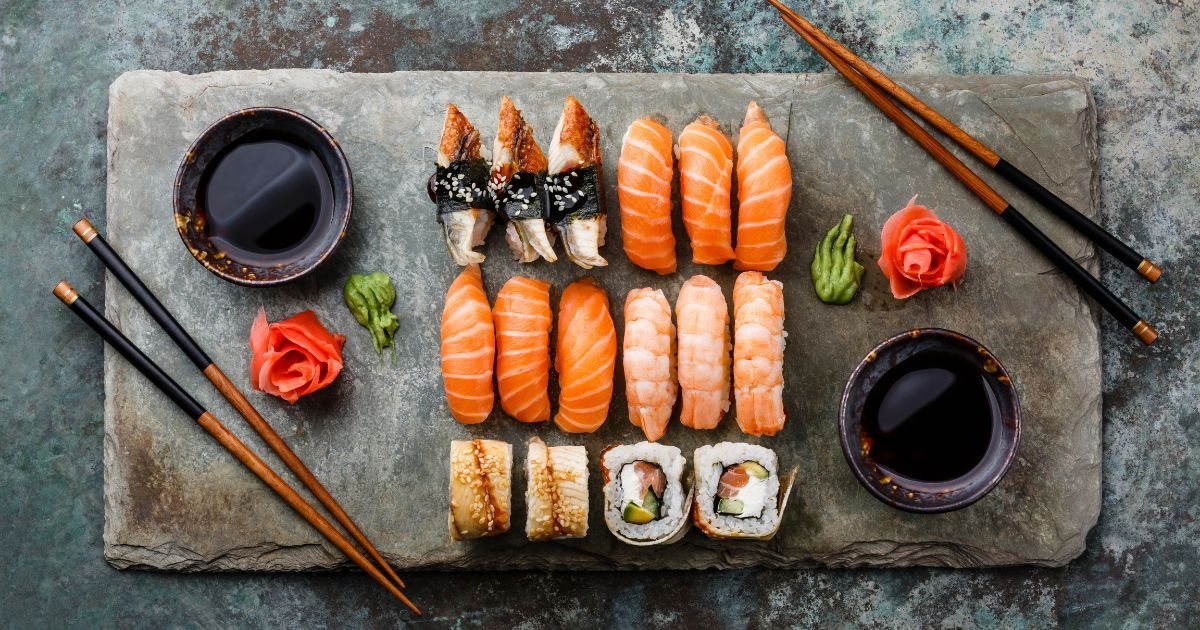

Seafood Delights
One of the easiest ways to get more astaxanthin is by eating more seafood. Grilled salmon, shrimp stir-fry, or a hearty crab salad - the options are as vast as the ocean! Remember, the redder the flesh, the higher the astaxanthin content.
Sushi Anyone?
Sushi is another delicious way to up your astaxanthin intake. Next time you're at your favorite sushi spot, order some salmon or shrimp rolls. They're not just tasty; they're packed with astaxanthin goodness.
Algae Supplements
If seafood isn't your thing, don't worry. You can also get astaxanthin from algae supplements. Add them to your smoothies for an antioxidant boost.

Astaxanthin Supplements
While getting nutrients from whole foods is always the best option, an astaxanthin supplement can be a convenient alternative, especially if you're allergic to seafood or follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- Astaxanthin supplements, typically derived from Haematococcus pluvialis algae, provide a concentrated dose of the antioxidant.
- It's important to remember that supplements should not replace a balanced diet but rather complement it.
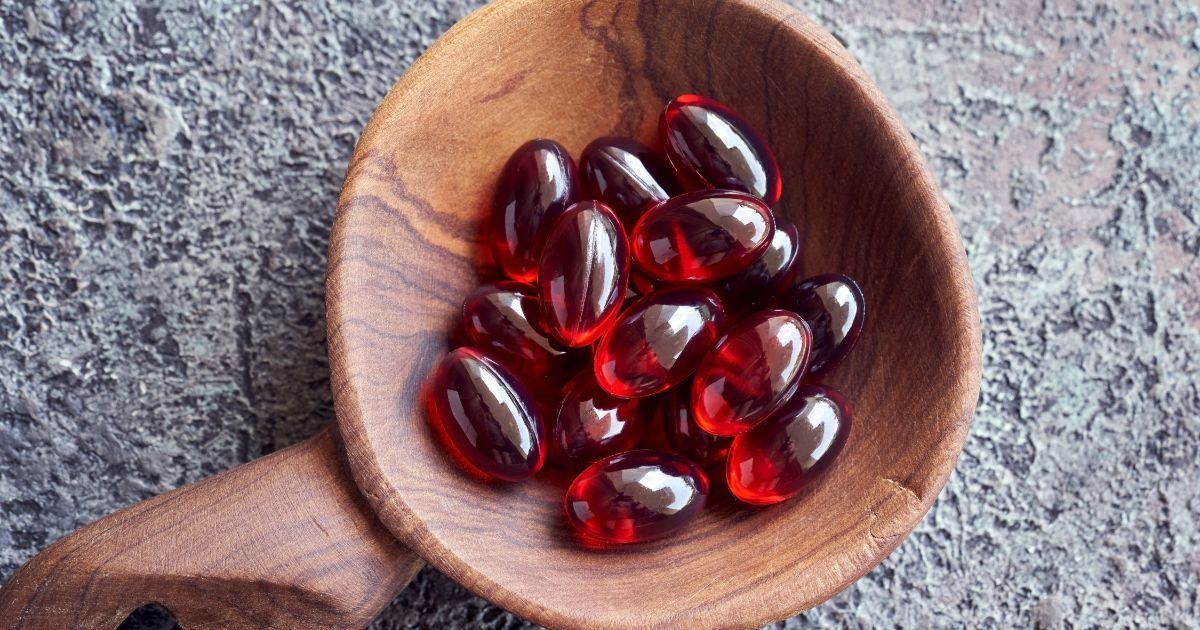

The benefits of taking astaxanthin supplements include convenience and a guaranteed amount of astaxanthin.
On the flip side, supplements can be costly, and they don't provide the additional nutrients you'd get from eating whole foods.
Synthetic vs Natural Astaxanthin
When it comes to astaxanthin, one important distinction you must be aware of is the difference between synthetic and natural sources.
Just like how a lab-grown diamond differs from one mined from the earth, synthetic and natural astaxanthin have their unique characteristics and impacts.
Synthetic Astaxanthin
Synthetic astaxanthin is produced chemically in labs. It's often used in aquaculture to give farmed salmon and trout their pinkish hue. When it comes to nutritional supplements for humans, synthetic astaxanthin might not be your best bet.
Research suggests that synthetic astaxanthin has less antioxidant power compared to its natural counterpart. Moreover, synthetic astaxanthin is composed almost entirely of a form that is less readily absorbed and used by the body.
Natural Astaxanthin
Natural astaxanthin, on the other hand, is derived from microalgae (Haematococcus pluvialis), yeast (Phaffia rhodozyma), or certain seafood and is considered superior due to its higher potency and bioavailability.
Plus, natural astaxanthin provides a mix of different forms, some of which are more easily utilized by the body.
What Should You Choose
While synthetic astaxanthin may be cheaper to produce, natural astaxanthin offers more bang for your buck in terms of health benefits.
- Whether you're choosing foods or supplements, it's worth going the extra mile to ensure you're getting natural astaxanthin.
Remember, it's always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. They can provide guidance based on your individual health needs and goals.
Bottom Line
Astaxanthin, the king of antioxidants, is a potent nutrient found in a variety of foods, particularly in seafood and certain types of algae.
From supporting skin health to boosting the immune system, the benefits of astaxanthin are impressive.
By incorporating astaxanthin-rich foods into your diet or considering astaxanthin supplementation, you're taking a positive step towards enhancing your overall health.
So why not add a splash of color to your plate and enjoy the health benefits of this amazing antioxidant? Your body will thank you!
Recommended For You...





